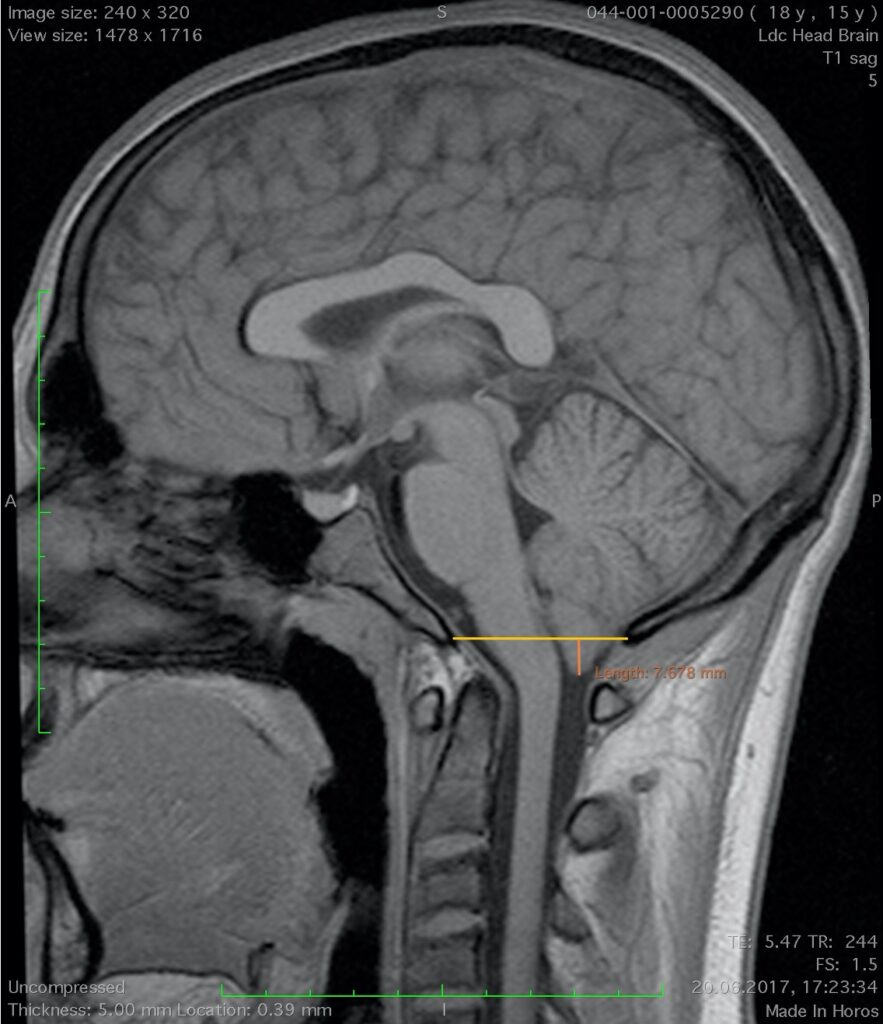
These are tumors and diseases of the spine and spinal cord at the level of the lower slopes, adjacent occipital bone, foramen magnum, and C1 C2 vertebrae. Chordomas, chondrosarcomas, meningiomas of the large occipital foramen are the most common among tumors. Taking into account
ventral localization of the chorda, chondrosarcoma of the craniovertebral junction, anterior approaches (transoral, endonasal) are important. At the same time, we use the endoscopic technique. Front (ventral) accesses are not only minimally traumatic and safe (the carotid arteries and vertebral arteries are located on the sides of the access) and make it possible to remove the tumor without manipulation, without possible traumatic damage to the brain stem and upper parts of the spinal cord. Meningiomas of the occipital foramen usually have an anterior-lateral position and in most cases require high lateral access. Removal of these tumors through a posterior approach is associated with the risk of possible brainstem injury. There are traumatic injuries C1 (Jefferson’s fracture) C2 (hangman, fractures of the odontoid process), a combination of C1 C2 fractures and their dislocations. Injury of C1 and C2 vertebrae, in the absence of neurological complications, is prognostically dangerous, as it is the cause of instability in the early or late periods, manifested by myelopathy, paralysis of the arms and legs, severe pain syndrome. Myelopathy, paralysis, basilar intussusception of C2 can also appear in the remote period of fractures of C1 and C2 vertebrae. Treatment can be both surgical and, in most cases, conservative. In the latter case, bony immobilization of the C1 and C2 vertebrae can be achieved with the help of the Halo device (Halo vest). The use of cervical collars (plastic, hipos, Philadelphia) is not effective in the treatment of fractures of the upper cervical spine. Surgical stabilization of C1 C2 pupils can be performed through a posterior approach using various stabilizing implants. At the same time, the compression of the brain stem and the upper parts of the spinal cord is due to the ventrally located bone fragments of the c1 c2 vertebrae. Surgical decompression can be achieved and should be performed only ventrally (transoral approach). Congenital anomalies of this level occur, in particular: Arnold-Chiari anomaly, platybasia, os odontoidea (tooth-shaped bone). Clinical symptoms of Arnold-Chiari are minimal, but depend on the degree of intussusception of the tonsils. Surgical treatment (geocompressive operations on the posterior cranial fossa if necessary C1 vertebra) is performed from the posterior approach. An important condition is not only bone decompression but also expansion of the dural sac (plastic dura mater). Decompressive surgery is also indicated for platybasia. Stabilizing operations are essential for osodontoidea.